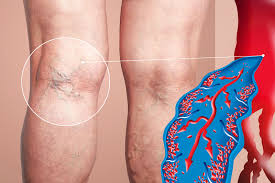
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) happens when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, usually in the legs. If left untreated, it can lead to serious complications like pulmonary embolism. Interventional radiology offers minimally invasive treatments to improve vascular health and lower these risks. Using advanced imaging, this approach is employed for procedures such as angiography, biopsies, drainage, and pain management.
Angiography to Manage DVT
Angiography is a key imaging tool in interventional radiology, providing detailed images of blood vessels. For patients suspected of having DVT, angiography can map out areas with restricted blood flow or clots. This is typically performed through venography, a specialized form of angiography that focuses on the veins. With real-time imaging, interventional radiologists can assess the severity and location of the clot.
One practical aspect of angiography lies in its guidance capabilities for subsequent treatments, such as catheter-directed thrombolysis. This procedure involves delivering clot-dissolving medications directly to the site, minimizing the impact on surrounding tissues. Angiographic imaging enhances precision, making interventional methods for DVT safer and more effective in targeted treatment.
Biopsies to Diagnose Conditions
Biopsies are often linked to diagnosing cancer, but they also play a role in investigating unusual cases of vascular diseases like DVT. Interventional radiologists use ultrasound or CT-guided techniques to collect tissue samples from affected areas. This helps rule out conditions such as cancer-related thrombosis, autoimmune disorders, or other issues that mimic or worsen DVT symptoms. Imaging guidance supports high accuracy, reduces complications, and improves diagnostic outcomes.
Drainage Procedures to Treat Complications
Drainage procedures are commonly used in interventional radiology to manage complications of DVT, such as post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS). Patients with PTS often experience swelling, pain, and ulcers in the affected limb due to impaired venous return. Using imaging, interventional radiologists can precisely place small catheters or devices to drain fluid buildup caused by venous insufficiency effectively.
These procedures can help alleviate immediate and long-term symptoms of PTS. They improve mobility and overall quality of life for individuals dealing with DVT-related challenges. Imaging-guided drainage techniques also have broader applications in other vascular conditions where fluid removal plays a therapeutic role.
Pain Management Techniques to Improve Recovery
Pain is a common symptom in patients with DVT, often caused by inflammation, vein pressure changes, or swelling. Interventional radiologists utilize advanced techniques to alleviate pain and enhance function. These include image-guided nerve blocks and selective ablation procedures that target pain-causing nerve fibers. These minimally invasive treatments offer faster recovery times compared to traditional surgery. When combined with other therapies, targeted pain management helps patients recover more comfortably and improves their overall treatment experience.
Taking the Next Step With Interventional Radiology
Interventional radiology offers targeted, minimally invasive approaches to manage deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and its associated complications. Each procedure is designed to improve patient outcomes. If you or someone you know is exploring treatment options for DVT, talk to a healthcare provider. They can explain how interventional radiology fits into a comprehensive care plan. Seeking expert care can significantly impact symptom management and overall quality of life.